France, officially the French Republic, is a unitary sovereign state comprising territory in western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. Metropolitan France extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea, and from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean.
Louis XIV made France the dominant cultural, political and military power in Europe, but by the late 18th century, the monarchy was overthrown in the French Revolution. France was governed as one of history’s earliest Republics until the Empire was declared by Napoleon, who dominated European affairs and had a long-lasting impact on Western culture.
Throughout its long history, France has produced many influential artists, thinkers, and scientists, and remains a prominent global center of culture. France remains a great power with significant cultural, economic, military, and political influence in Europe and around the world. It is a developed country with the world’s fifth/sixth-largest economy by nominal GDP and tenth-largest by purchasing power parity. In terms of total household wealth, France is the wealthiest nation in Europe and fourth in the world.
French citizens enjoy a high standard of living, and the country performs well in international rankings of education, health care, life expectancy, civil liberties, and human development. France is a founding member of the United Nations. France is a founding and leading member state of the EU.
Why Study in France?
- High Visa Success Rate
- Easy & Streamlined Visa Process
- 2 Years Work Permit After Study [APS]
- Study Programs Available with Internship
France Education System
The French educational system is highly centralized and organized, with many subdivisions. After nursery school or kindergarten (école maternelle), which is optional, the French compulsory education system is divided into three stages or cycles which are Primary Education, Secondary Education, and Higher education.
Primary Education (enseignement primaire)
Children in France attend primary school from Age of 6 to 11 years.
There are 5 levels of Primary Education.
- Cours préparatoire (CP) or 11ème : Age 6 to 7 years
- Cours élémentaire (CE1) or 10ème : Age 7 to 8 years
- Cours élémentaire (CE2) or 9ème : Age 8 to 9 years
- Cours moyen 1 (CM1) or 8ème : 9 to 10 years
- Cours moyen 2 (CM2) or 7ème : 10 to 11 years
Secondary Education (enseignement secondaire)
Between the ages of 11 and 15, students in France attend a middle school or collège.
There are 4 levels of Secondary Education.
- 6ème : 11 to 12 years
- 5ème : 12 to 13 years
- 4ème : 13 to 14 years
- 3ème : 14 to 15 years
Higher Education
Students generally prepare themselves for Higher Education at the Age of 15 to 18 years.
Last 3 years of secondary education are spent as a lycée general, a lycée technique or a lycée professionnel. Students take the same core curriculum of some 8 or 9 subjects but are offered three electives and an artistic workshop. At the end of this year, the key decision is made as to which baccalaureat the student will pursue. The levels are:
- Seconde (CAP, BEP) : 15 to 16 years
- Première (CAP, BEP) : 16 to 17 years
- Terminale (BAC) : 17 to 18 years
Lycée General and Lycée Technique
Students start to specialize with the aim of sitting the Baccalauréat (le bac), which is the qualification to enter university at 18 years old. Students choose different ‘series’. The general bac consists of the L series (literary studies), ES series (economic and social studies) or S series (sciences).
Lycée Professionnel
The professional baccalaureate requires three years of study and certifies the student to work in a qualified professional industry.
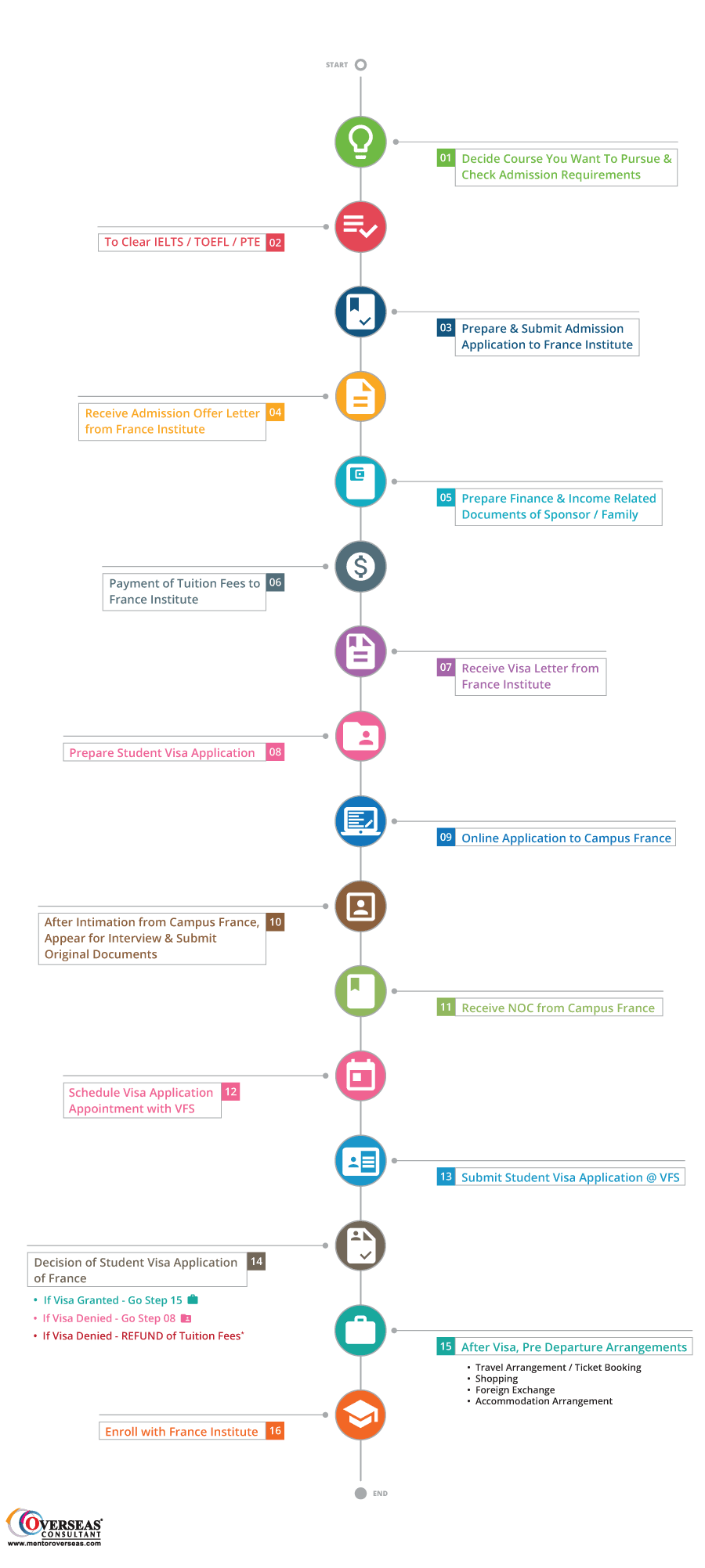
France Visa Process